9000-11-7
(general for cellulose derivatives; specific functional groups may vary)
CelloPAC
Hicell
MoNPAC
Tel-polymer
Stable up to 150oC (short term),
Long term stability at≤120oC
Compatibility: Works with most ionic/nonionic additives (e.g., xanthan gum, starch).
Electrolyte Resistance: Maintains viscosity in high-salinity brines (e.g., NaCl, CaCl₂).
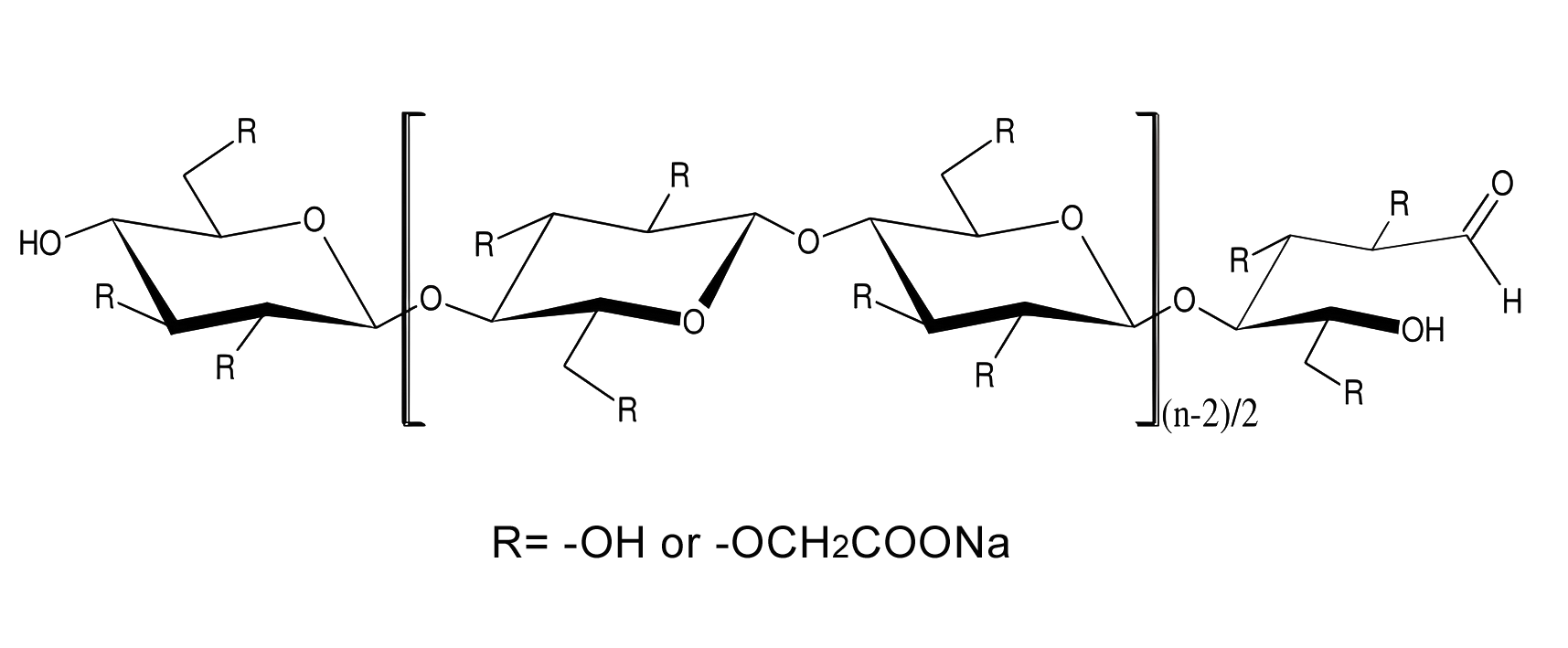
Polyanionic Cellulose (PAC) is a water-soluble anionic polymer derived from the chemical modification of natural cellulose. Widely used in oil drilling, construction materials, food, and pharmaceutical industries, PAC is valued for its exceptional thickening, suspension, salt tolerance, and thermal stability properties.
Oil Drilling Fluids:
Acts as a viscosifier and fluid loss control agent in high-temperature/high-salinity conditions (e.g., shale gas, deep-well drilling).
Construction Materials:
Additive in cement/mortar to improve water retention, workability, and anti-settling properties.
Food Industry:
Food-grade PAC (E469) as a stabilizer/thickener (e.g., dairy products, ice cream).
Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics:
Tablet binder or emulsion stabilizer (shampoos, skincare products).
PAC is classified by substitution degree (DS) and purity:
Low-Viscosity: For low-solids drilling fluids.
High-Viscosity: For high-performance fracturing fluids.
Ultra-High Purity: Used in sensitive applications (e.g., pharmaceuticals).
25kg/polybag, or fiberdrum.
Available custom package.